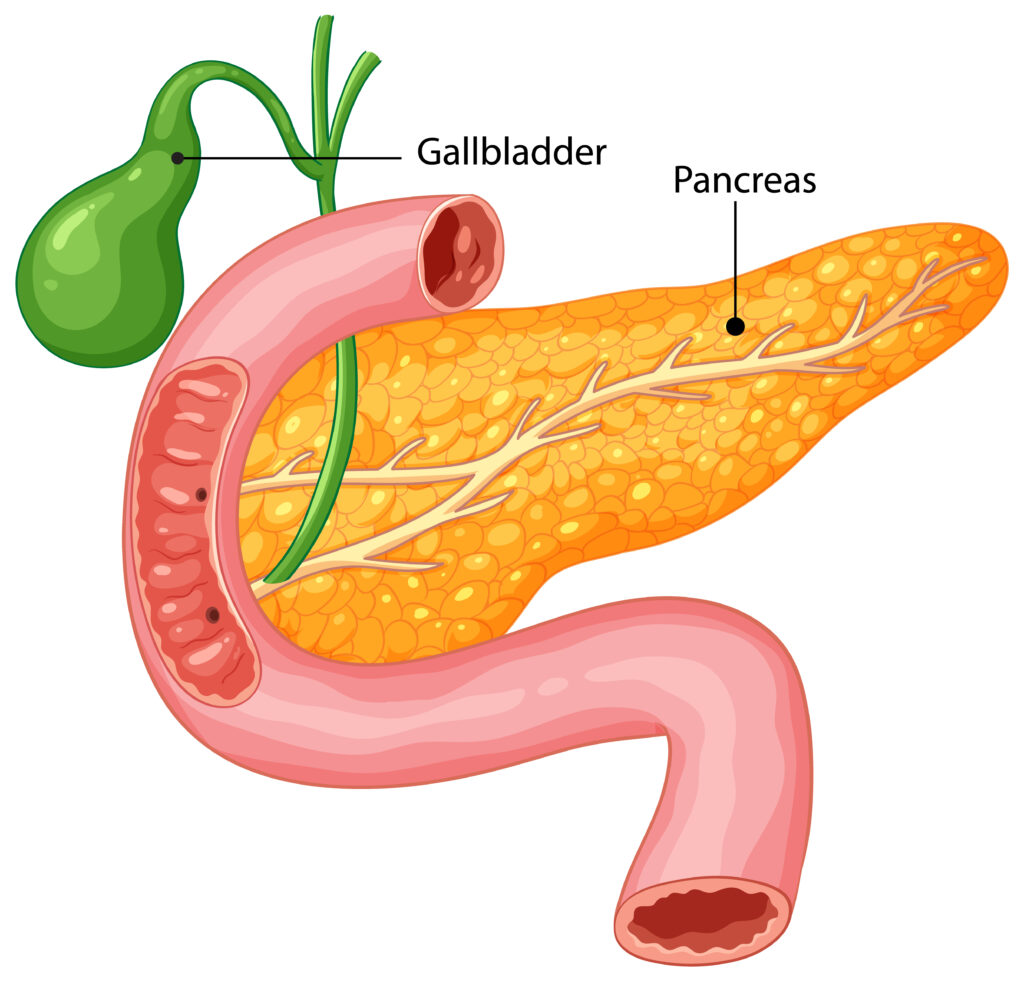
Introduction:
The gallbladder is a small pear-shaped organ located beneath your liver. Its job is to store and release bile, a digestive fluid that breaks down fats. While this is not essential for survival, ignoring gallbladder symptoms can lead to painful and even life-threatening conditions. In this article, we will discuss common issues, how to recognize them, when to seek emergency help and the best treatments available.
Common Gallbladder Problems
- Gallstones (Cholelithiasis)
Gallstones are solid deposits of bile salts and cholesterol. They can range from tiny grains to large stones. When a stone blocks the bile duct, it triggers sharp abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting. This discomfort is not limited to the stomach many patients experience referred pain in the right shoulder or back.
- Gallbladder Inflammation (Cholecystitis)
Inflammation usually develops due to gallstones but can also result from infections. Patients often ask what antibiotics treat infection commonly prescribed ones include ceftriaxone, metronidazole or ciprofloxacin depending on severity. If untreated, inflammation can cause tissue damage and sepsis.
- Gallbladder Attack (Biliary Colic)
A gallbladder attack happens when a gallstone temporarily blocks the bile duct, causing sudden and severe abdominal pain. Knowing when to go to hospital for gallbladder attack is crucial. Seek emergency care if pain lasts longer than two hours, if fever develops or if the skin/eyes turn yellow (jaundice).
- Gallbladder Polyps
Polyps are growths inside the gallbladder wall. Most are harmless but larger ones may require monitoring or surgical removal because they can sometimes turn cancerous.
- Gallbladder Cancer (Rare but Serious)
Though uncommon, cancer is often diagnosed late because symptoms mimic other gallbladder issues. Persistent abdominal pain, unexplained weight loss and jaundice should be taken seriously.
Recognizing the Signs of Gallbladder Problems
This organ disease presents differently in each person. Some have mild symptoms, while others experience severe attacks. Key signs of problems include:
- Intense pain in the upper right abdomen
- Pain radiating to the right shoulder or back.
- Bloating, gas, or indigestion after meals
- Fever and chills in case of infection
- Vomiting and nausea
- Yellowing of skin or eyes (jaundice)
How long after eating does gallbladder pain start?
Typically, 30 minutes to 1 hour after eating fatty, fried or oily meals.
Treatment Options
Lifestyle and Non-Surgical Management
- Dietary changes: Avoid fried and high-fat foods and eat smaller, balanced meals.
- Weight management: Obesity increases the risk of gallstones.
- Medications: In rare cases, drugs may help dissolve gallstones, though they are slow and not always effective.
- Antibiotics: If infection is present, your doctor may prescribe targeted antibiotics.
Surgical Treatment
If gallbladder disease becomes recurrent or severe, removal surgery (cholecystectomy) is recommended. It is one of the most common and safe surgical procedures worldwide.
Diet after gallbladder removal is critical for recovery. Patients should eat:
- Low-fat meals
- Lean proteins such as chicken and fish
- High-fiber foods like fruits, vegetables and whole grains
- Small, frequent meals instead of large portions
Frequently Asked Questions
- What are the first signs of gallbladder problems?
Bloating, indigestion, nausea and upper right abdominal pain are common early signs. - Where does referred pain occur?
It often radiates to the right shoulder, mid-back or between the shoulder blades. - When should I go to hospital for gallbladder attack?
If pain lasts longer than 2 hours, is severe or is accompanied by fever, nausea or jaundice. - Can pain come and go?
Yes, it often occurs after eating fatty meals and may subside on its own. - How long after eating does pain start?
Usually 30 minutes to 1 hour after a heavy or greasy meal. - What antibiotics treat this organ’s infection?
Doctors may prescribe ciprofloxacin, metronidazole or ceftriaxone, depending on the infection type. - Is surgery always required for gallbladder problems?
Not always. Mild cases can be managed with diet and medications, but surgery is the only permanent solution for gallstones. - What is the recovery time after gallbladder removal?
Most patients return to normal activities within 1 to 2 weeks, though full recovery may take up to a month. - What diet after gallbladder removal is recommended?
Low-fat meals, high fiber and small, frequent portions help in smooth digestion. - Can untreated gallbladder problems be dangerous?
Yes. Ignoring symptoms can lead to infection, gallbladder rupture or even life-threatening complications like sepsis.
Conclusion:
Gallbladder issues are more common than people think and they often begin with mild digestive problems. Recognizing the signs of gallbladder problems, understanding when to go to hospital for gallbladder attack and following a proper diet after gallbladder removal can protect you from severe complications. If you experience persistent symptoms, consult a healthcare professional immediately. Your digestive health depends on timely care.